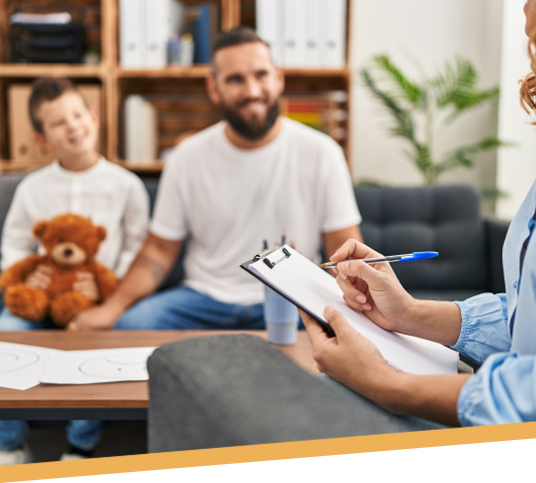
Eating disorders are complex mental health conditions that affect people around the world. These disorders often involve abnormal or disrupted eating patterns, which can lead to significant physical and emotional challenges. Treatment for disordered eating typically requires a multidisciplinary approach, as it addresses psychological, nutritional, and sometimes medical needs. Here is some information about commonly used evidence-based treatments for eating disorders.
Medication Management
Managing medication can play a key role in treating an eating disorder, especially when anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive traits are present. While no medication can directly cure disordered eating, some, like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can help. These medications have been found to improve mood and reduce binge-eating episodes. By stabilizing symptoms, medication can make it easier for individuals to fully participate in other treatments, such as therapy and counseling.
Medication is just one part of a broader treatment plan. Regular monitoring by medical professionals helps track progress and adjust prescriptions as needed. Working closely with psychiatrists and primary care doctors supports both mental and physical health throughout the recovery journey.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy is widely regarded as a leading treatment for disordered eating. This evidence-based therapy focuses on identifying and challenging unhelpful thoughts and behaviors linked to eating, body image, and self-worth. Individuals with anorexia nervosa may work on reframing beliefs surrounding food restriction and control, while those with binge-eating disorder may address patterns of guilt associated with overeating.
The structured, goal-oriented nature of CBT makes it highly effective in managing the symptoms of disordered eating. Sessions often include practical exercises to develop new coping mechanisms and healthier thought processes. Research also shows that CBT’s ability to reduce the likelihood of relapse makes it a valuable long-term strategy for recovery.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) is an effective approach to treating eating disorders. ACT focuses on accepting thoughts and emotions without judgment. It helps individuals build psychological flexibility and take actions aligned with their values. ACT can help reduce struggles with body image and food. By promoting acceptance, it lessens the grip of perfectionism and self-criticism, allowing individuals to focus on meaningful, fulfilling activities.
Nutrition Counseling
Nutrition counseling is key to treating disordered eating by addressing the physical effects of disordered eating. Registered dietitians help clients rebuild a healthy relationship with food through education, meal planning, and correcting dietary misconceptions. Intuitive eating strategies focus on recognizing hunger and fullness cues while building confidence in food choices. This supportive process promotes physical recovery and restores a positive connection to eating.
Nutrition counseling can also help individuals develop coping strategies for dealing with triggers or stressful situations that may lead to disordered eating behaviors. This may include developing a meal plan or creating a list of alternative activities to turn to when feeling overwhelmed. Over time, these strategies can help promote healthier habits and improve overall well-being.
Take the First Step in Eating Disorder Recovery
Disordered eating recovery is a deeply personal process, but it is achievable with the proper support and resources. Seeking assistance from licensed mental health professionals, registered dietitians, and medical providers is a valuable first step toward lasting recovery. Reach out to a trusted treatment provider today to learn more about creating a customized care plan tailored to your unique needs.
- Braces for Adults and What You Need to Know
- Benefits of Invisible Braces for Teens and Adults
- Understanding the Link Between Behavioral Studies and Mental Health Support Services
- Key Characteristics That Support Long-Term Success in Nursing
- How Continued Nursing Education Supports Safer and More Effective Healthcare






Leave a Reply